硫作为植物必需的营养元素,在草地生态系统养分循环中起到重要作用,但过量施硫肥或大气硫沉降是陆地生态系统土壤酸化的主要因子,可造成土壤盐基流失、养分失衡,并对土壤生物群落结构及功能产生影响。在过去的几十年中,关于氮沉降对草地土壤酸化及生态系统影响方面已有诸多研究,但关于硫沉降对草地生态系统生物区系影响方面的研究相对缺乏。
沈阳生态所土壤化学组依托额尔古纳森林草地过渡带生态研究站2017年5月建立的草地硫添加试验平台(硫添加量分别为0、1、2、5、10、15、20、50 g S m-2 yr-1),2019年9月对表层土壤的相关化学及生物学性质进行了调查取样及测定分析,研究发现硫添加对土壤线虫丰度及多样性具有显著影响,但对土壤线虫总量及优势种(Cervidellus和Aphelenchus)的相对丰度无显著影响;相关分析及结构方程模型显示,硫添加会显著增加捕食-杂食类群线虫的相对丰度,降低食细菌类群线虫的相对丰度,指示食物网结构的结构指数随硫添加量的增加而显著增加。硫沉降主要通过影响线虫捕食杂食类群来改变自上而下的捕食压力来影响草甸土壤线虫群落结构(图1)。研究结果表明硫酸沉降可能会改变土壤线虫群落组成、影响线虫群落结构稳定性,进而增加对地下生态系统和各营养级间能量流动的扰动。
上述结果以Sulfur deposition changed the community structure of soil nematodes by affecting omnivores-predators为题发表在Science of the Total Environment(2021, 771: 144912)上。土壤化学组研究助理张爱林(现中国科学院新疆生态与地理研究所博士研究生)为论文的第一作者,姜勇研究员为通讯作者。该研究得到国家自然科学基金面上项目(31870441、32071563)资助。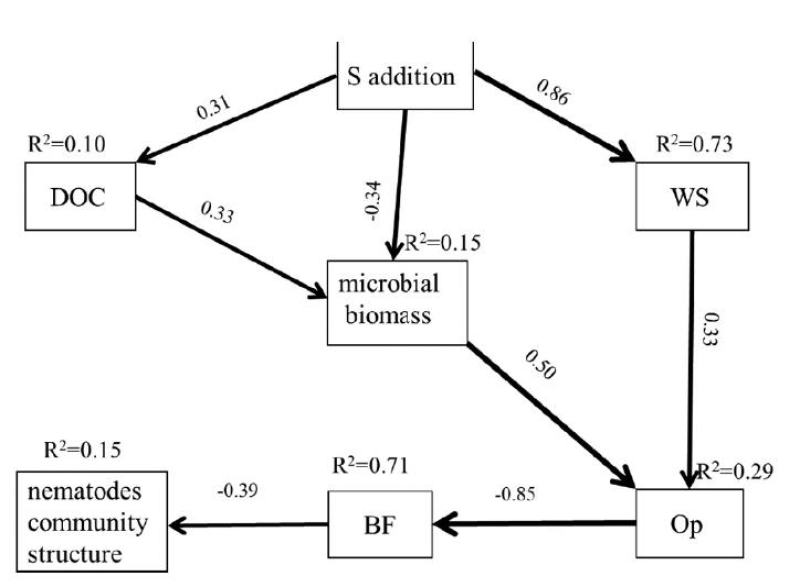
上述结果以Sulfur deposition changed the community structure of soil nematodes by affecting omnivores-predators为题发表在Science of the Total Environment(2021, 771: 144912)上。土壤化学组研究助理张爱林(现中国科学院新疆生态与地理研究所博士研究生)为论文的第一作者,姜勇研究员为通讯作者。该研究得到国家自然科学基金面上项目(31870441、32071563)资助。

图1 硫添加对土壤理化性质、微生物生物量、线虫群落组成及丰富度影响的结构方程模型
(The models fit the data well: χ2 = 10.375, p = 0.663, AIC = 40.375, RMSEA < 0.001, CFI = 1.000, GFI = 0.933. Numbers adjacent to arrows are the standardized path coefficients (equivalent to correlation coefficients). Arrow thickness indicate the strength of the relationships. Solid arrows denote significant effects (P < 0.1) or marginally significant (0.05 < P < 0.01) effects, the direction of arrows represents top–down and bottom–up forces; R2 values associated with response variables indicate the variance accounted for by the mode. Non-significant paths are removed in the final model. Microbial biomass: the first principal components (PC1) of MBC, MBN, MBP; BF: Bacterivores (Ba) and Fungivores (Fu);Nematodes community structure: the first principal components (PC1) of SR, H', λ, J'.)





